Post Date: September 10, 2023

Cybersecurity has become paramount for individuals and organizations in today’s digitally interconnected world. This comprehensive guide provides valuable insights into the dynamic field of cybersecurity, covering various topics including the cyber threat landscape, malware and ransomware, network and cloud security, social engineering, incident response, cybersecurity frameworks, legislation and compliance, ethical hacking, cybersecurity for small businesses, data privacy, multi-factor authentication (MFA), IoT security, mobile device security, the zero trust security model, phishing and email security, endpoint security, cybersecurity awareness training, supply chain security, cyber insurance, emerging technologies and threats, and the dark web’s role in cybercrime. By understanding these critical aspects, you can take proactive steps to safeguard your digital assets effectively.
The Important Points
1. Cyber Threat Landscape:

The cybersecurity landscape is in a constant state of flux, with new threats emerging regularly. From state-sponsored attacks to sophisticated criminal enterprises, staying informed about the current threat landscape is the foundation of robust cybersecurity.
2. Malware and Ransomware:

Malware, including ransomware, is a pervasive threat. This section explores different types of malware and provides strategies for prevention and recovery.
3. Network Security:
Networks are prime targets for cybercriminals. Learn about network security measures like firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and network segmentation.
4. Cloud Security:
As organizations migrate to the cloud, securing cloud environments becomes critical. Discover the challenges and best practices for cloud security.
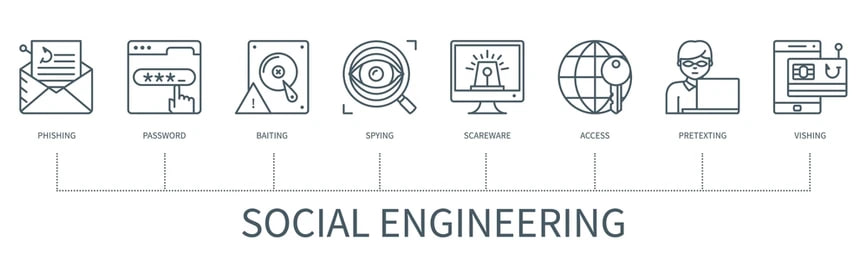
5. Social Engineering:
Social engineering attacks manipulate human psychology. This section delves into various social engineering techniques and how to defend against them.
6. Incident Response and Cybersecurity Frameworks:
Swift and effective incident response is crucial. Learn how organizations can prepare for and respond to incidents and explore popular frameworks like the NIST Cybersecurity Framework and ISO 27001.
7. Cybersecurity Legislation and Compliance:
Compliance with cybersecurity regulations is mandatory for many organizations. Understand the impact of laws like GDPR, HIPAA, and CCPA on cybersecurity practices.
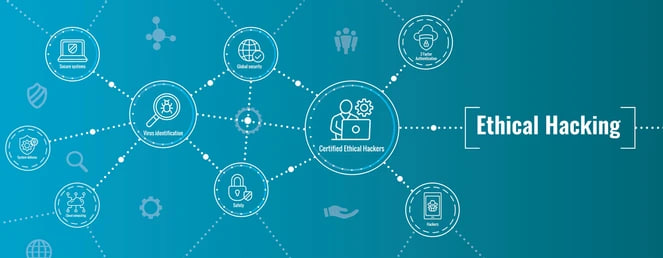
8. Ethical Hacking and Penetration Testing:
Ethical hackers and penetration testers identify vulnerabilities. Discover the importance of ethical hacking and its role in bolstering security.
9. Cybersecurity for Small Businesses:
Small businesses are not immune to cyber threats. Learn how SMBs can implement cost-effective cybersecurity measures to protect their operations.
10. Data Privacy and Protection:
Data privacy and protection are integral to cybersecurity. Explore strategies for securing sensitive data, including encryption and access controls.
11. Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA):
MFA enhances authentication security. Learn how to implement MFA for various applications and accounts.
12. IoT (Internet of Things) Security Challenges:
IoT devices present unique security challenges. Understand the risks and how to mitigate them.
13. Mobile Device Security:
Mobile security is essential. Explore threats and best practices for securing smartphones and tablets.
14. Zero Trust Security Model:
Zero trust security is a paradigm shift. Learn the principles and how to implement them.
15. Phishing and Email Security:
Phishing attacks are common. Discover tips for recognizing and defending against them.
16. Endpoint Security:
Secure endpoints are critical. Explore antivirus software, EDR, and application whitelisting.
17. Cybersecurity Awareness Training:

Educating employees is vital. Learn about effective cybersecurity awareness training programs.
18. Supply Chain Security:
Third-party vendors pose risks. Discover strategies for securing the supply chain against cyber threats.
19. Cyber Insurance:
Cyber insurance helps in recovery. Understand key considerations when selecting a policy.
20. Emerging Technologies and Threats:
Explore the impact of technologies like 5G, quantum computing, and AI/ML on cybersecurity and potential future threats.
21. Dark Web and Cybercrime Underground:

The dark web harbors cybercriminal activities. Learn how organizations can monitor it for potential threats.
Conclusion:
Cybersecurity is an ever-evolving field that demands constant vigilance and adaptation. By understanding the vast array of topics covered in this comprehensive guide, you can take proactive steps to safeguard your digital assets. In a world where cybersecurity is paramount, staying informed and prepared is your best defense against the evolving threats of the digital age.







